Bridging Domotz to Cloud Hosted Functions for Triggering API
Using serverless Python functions to handle network events is an incredibly efficient way to extend your monitoring capabilities. Below, we’ll configure a DigitalOcean Function to ingest a "Device Down" event and automatically trigger a power cycle via the Domotz API.
1. DigitalOcean Infrastructure Setup
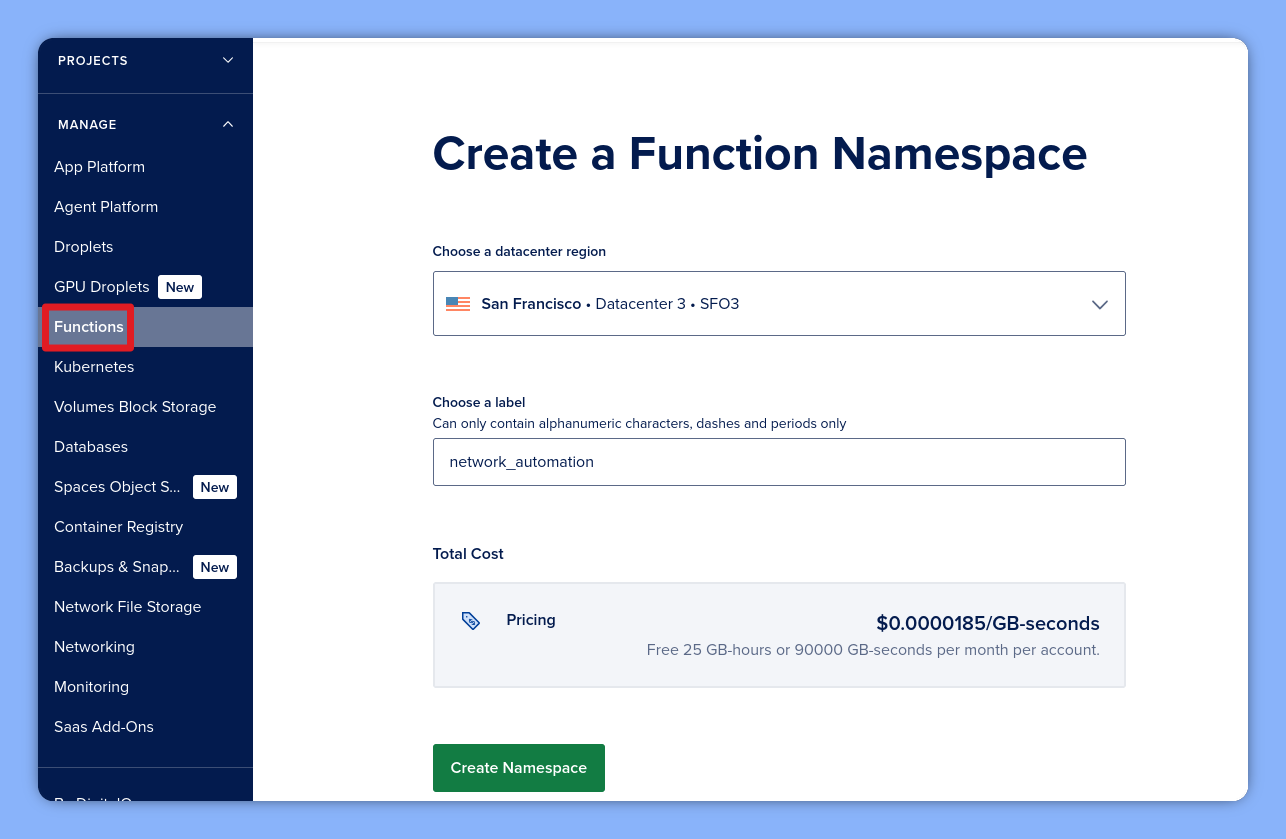
A. Create the Namespace
First, we need to create a namespace to house our automation. Navigate to the Functions tab and click Create Namespace to initialize your namespace.
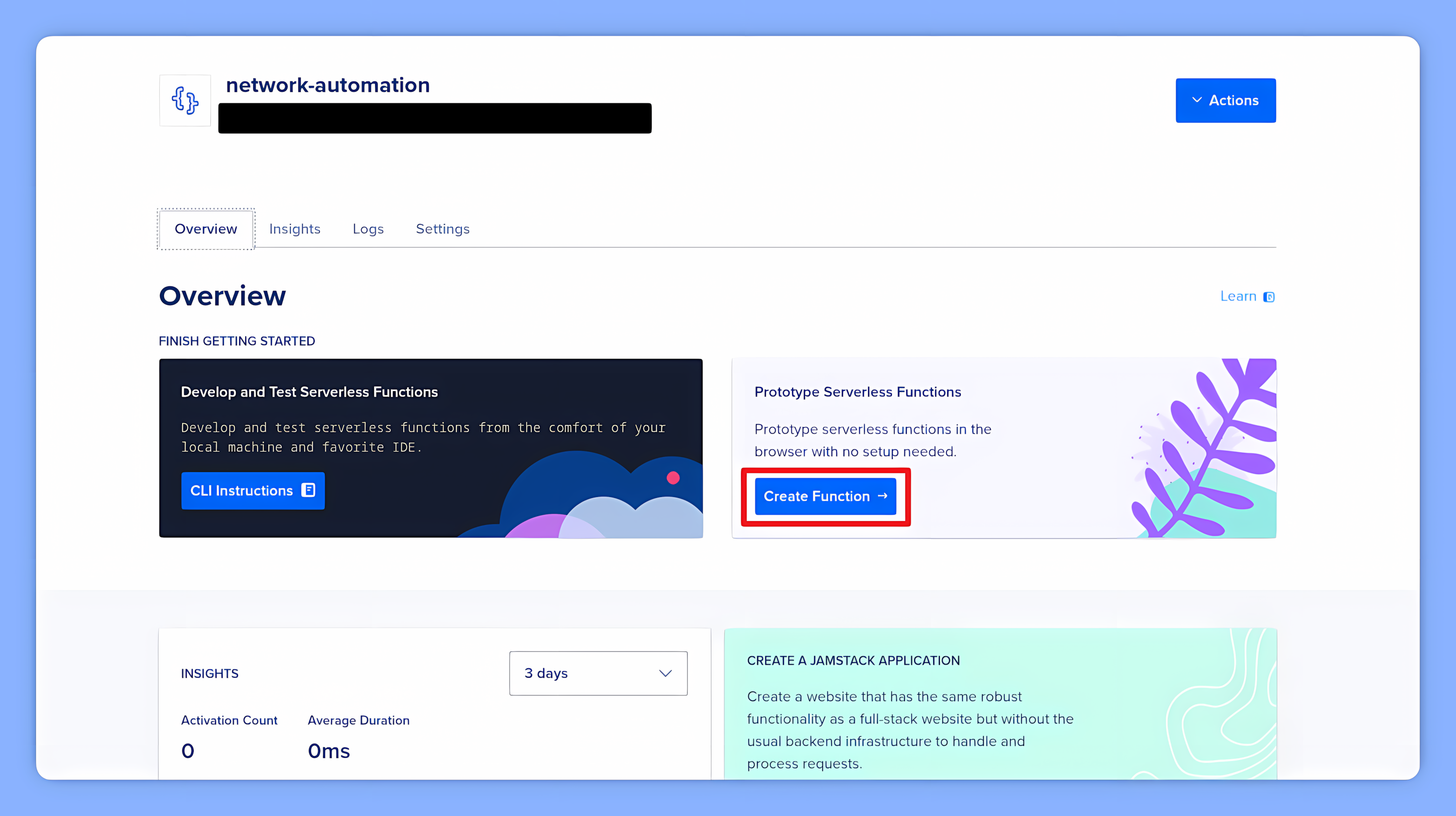
B. Add the Function
Once your namespace is ready, click Create Function. Select the Python runtime and name your function (e.g., domotz-reboot).
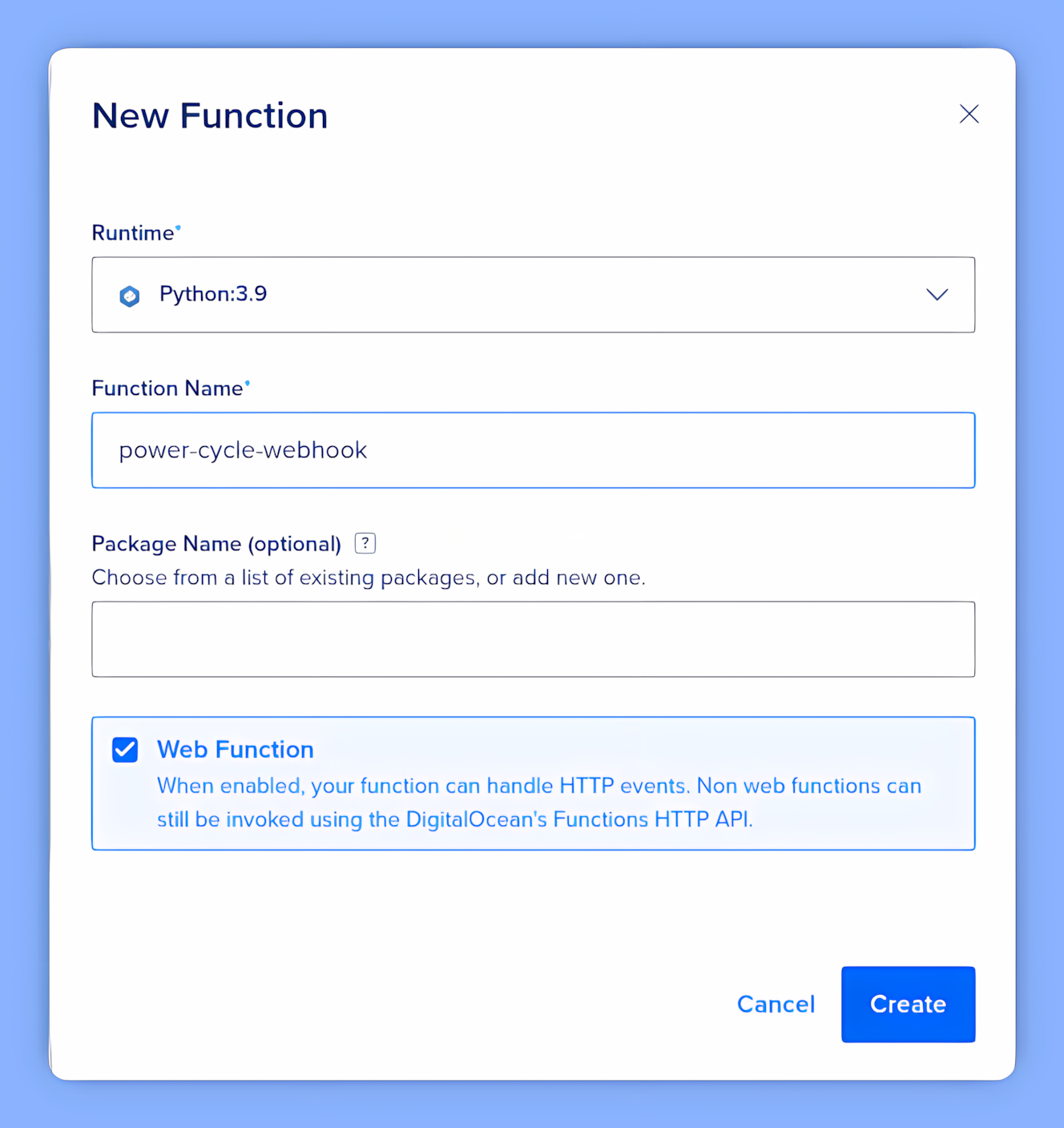
C. The Logic: Python Script
Now, replace the default code with this logic. This script extracts the agent and device IDs from the Domotz payload and triggers the power cycle action.
import os
import requests
def main(args):
# 1. Get Environment Variables
base_url = os.getenv('DOMOTZ_BASE_URL', '').rstrip('/')
api_key = os.getenv('DOMOTZ_API_KEY')
# 2. Extract nested data from the payload
event_data = args.get('data', {})
agent_id = event_data.get('agent_id')
device_id = event_data.get('device_id')
status = event_data.get('value') # e.g., "DOWN"
print(f"Webhook Received: Agent {agent_id}, Device {device_id}, Status: {status}")
# 3. Only proceed if the device is DOWN and IDs exist
if status == "DOWN" and agent_id and device_id:
url = f"{base_url}/agent/{agent_id}/device/{device_id}/action/power/cycle"
headers = {
"X-Api-Key": api_key,
"Accept": "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
try:
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers)
return {"statusCode": 201, "body": {"message": "Reboot command sent"}}
except Exception as e:
return {"statusCode": 500, "body": {"error": str(e)}}
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": {"message": "No action taken"}}2. Configuring Environment Variables
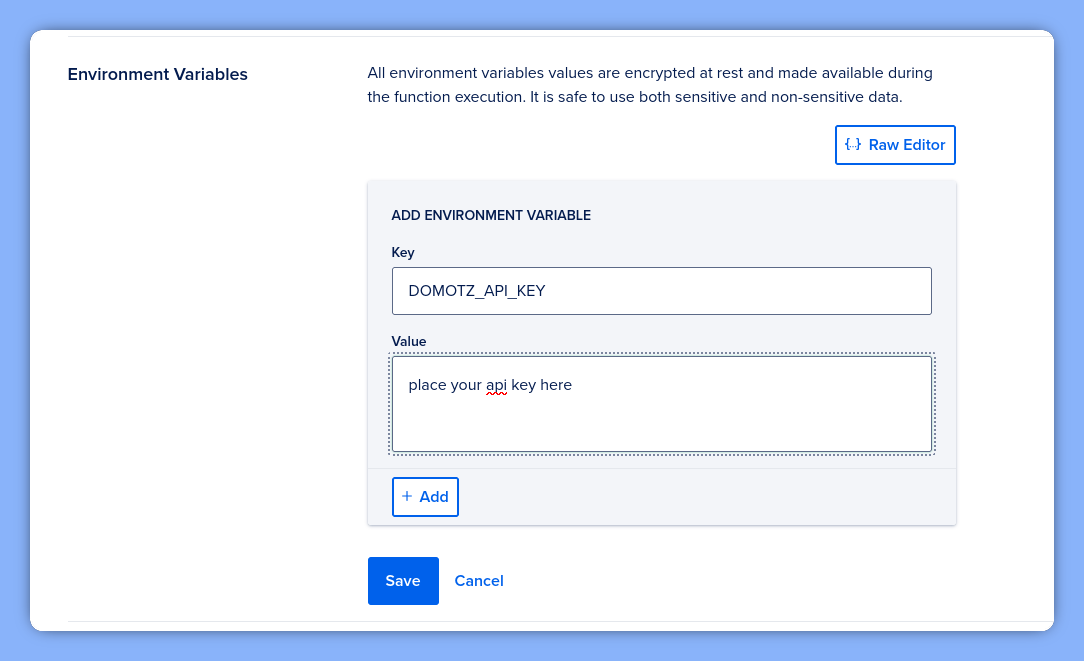
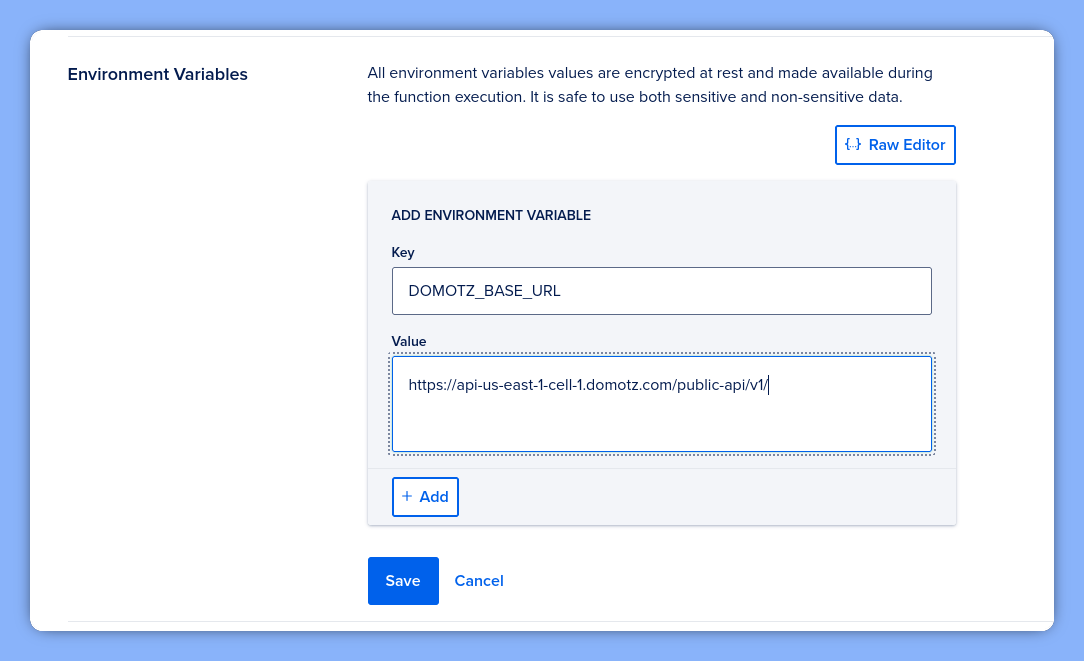
To make the script work, we must define our secure variables. Navigate to the Settings tab of your function.
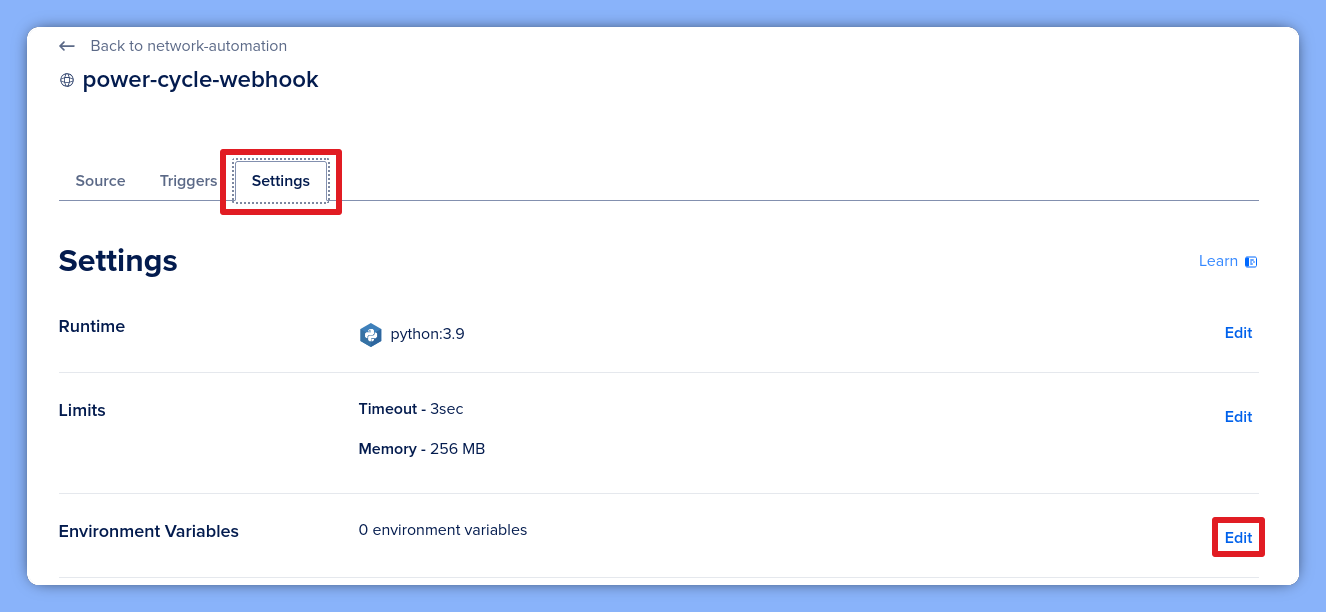
Add DOMOTZ_API_KEY and DOMOTZ_BASE_URL here. Additionally, ensure you grab your Web Function URL and verify the toggle is enabled so Domotz can reach the endpoint.
3. Domotz Configuration
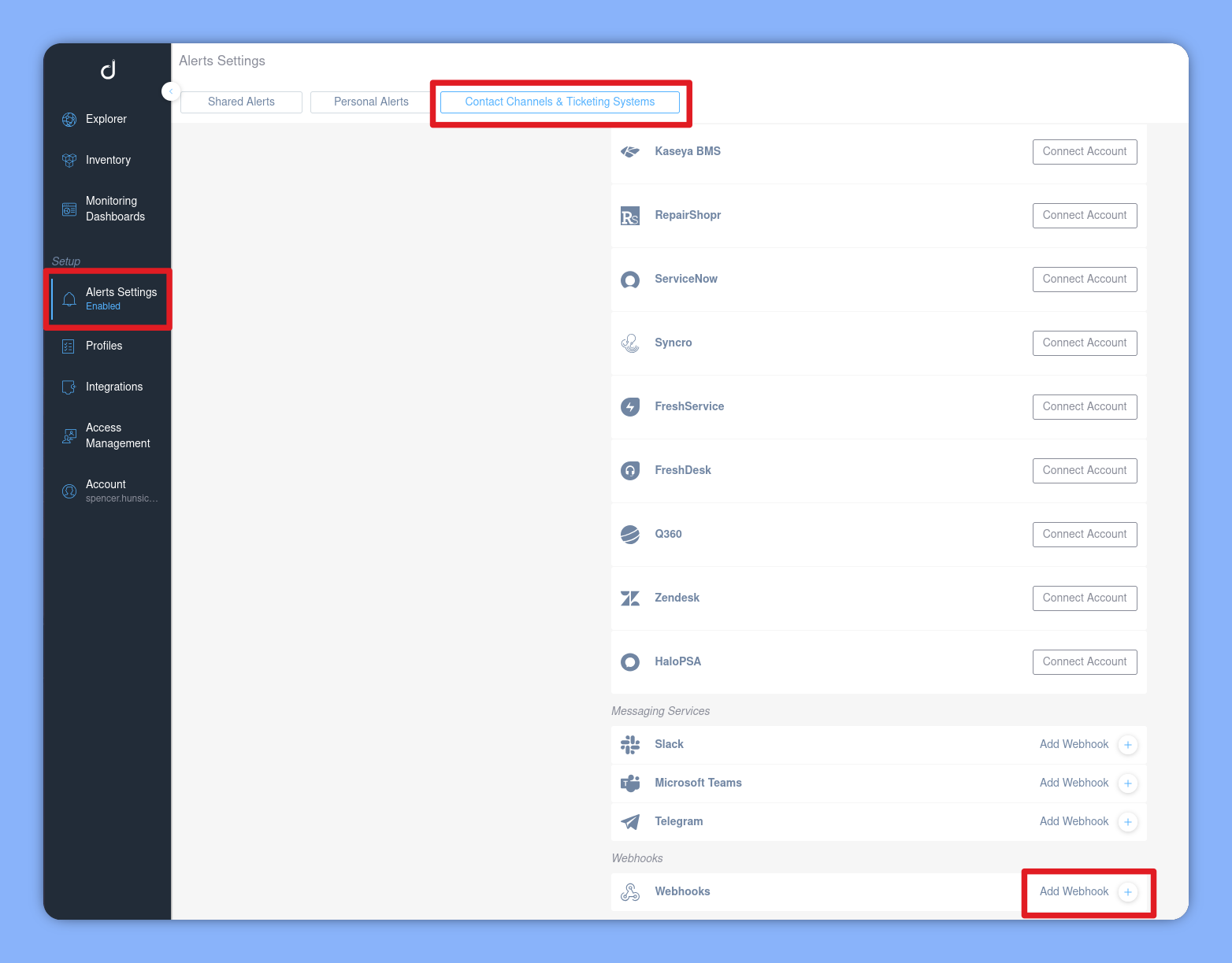
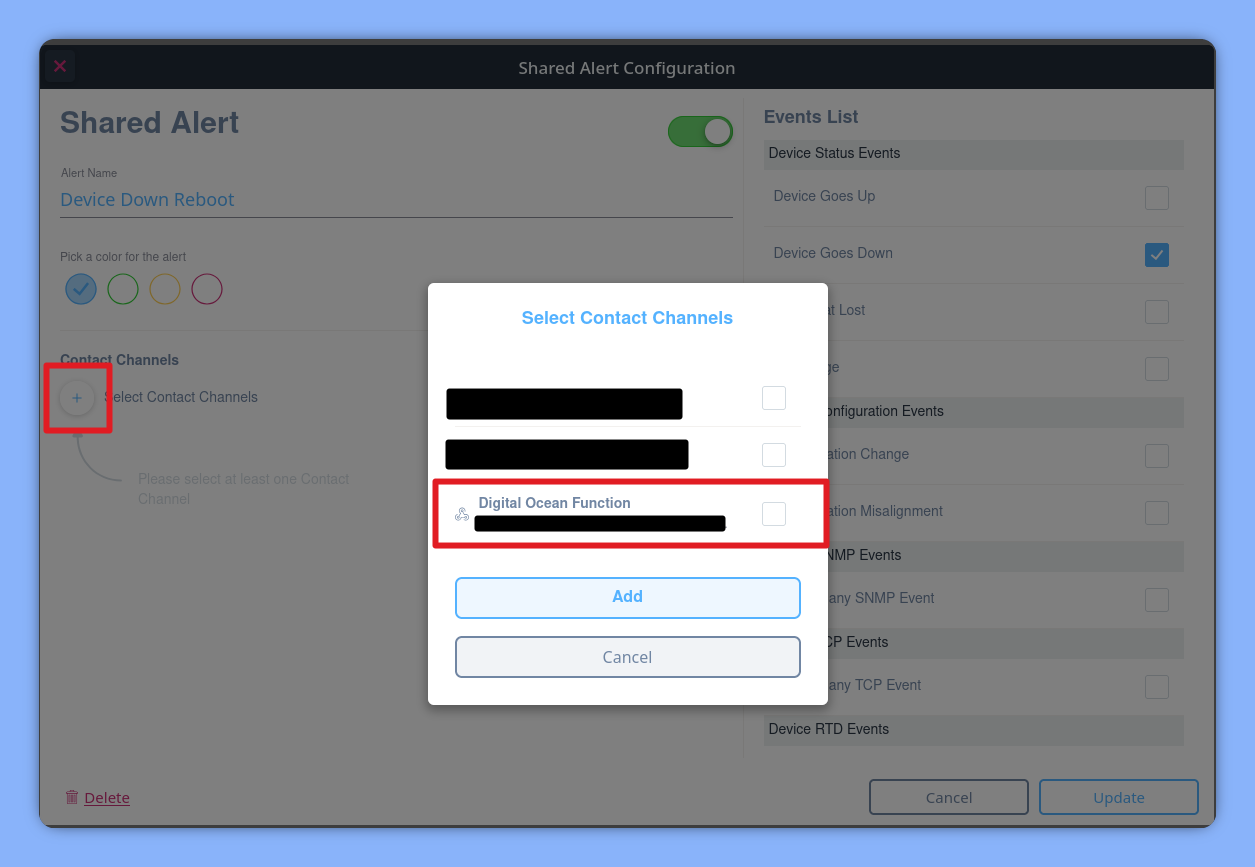
Finally, point Domotz to your new cloud function by creating a Webhook channel with the URL from the previous step.
4. Verification
You can verify the trigger is reaching your function by running the following in your terminal:
doctl serverless activations logs --follow --function your-function-name